1. BASIC
2. RIS (Remote Installation Services)
3. NETWORK
Basic installation is through a CD key and Options that we choose
Remote Installation Services:RIS supports two types of operating system images:
§
CD-based images (images created by using RISetup)§
Remote Installation Preparation (RIPrep) images.
The CD-based option is similar to setting up a server operating system directly from the Windows Server 2003 product CD, except that the source files reside on a RIS server.
You can create a RIPrep image from a server that is running Windows Server 2003 with SP2, and you can then deploy this image to other similar servers that are connected to the network.
Creating a CD-based (RIS setup) image to add to a RIS server
After you install RIS, perform the following steps to create the image and then add the image to your RIS server.
To create an image of Windows Server 2003 with SP2 and add it to your RIS server
1. Create an integrated version of the operating system with SP2.
2. To create an image, click Start, click Run, and then type: risetup.exe /add
3. The Remote Installation Services Setup Wizard appears. Follow the instructions in the wizard. When the Installation Source Files Location page prompts you for the image source, enter the path to the shared folder that contains the integrated version that you created in Step 1.
4. A box appears showing the progress of the installation. After the RISetup image is complete, you can install the image on each server as described in Remote Installation Services on the Microsoft TechCenter Web site.
Creating a CD-based (RIS setup) image to add to a RIS server
After you install RIS, perform the following steps to create the image and then add the image to your RIS server.
To create an image of Windows Server 2003 with SP2 and add it to your RIS server
1. Create an integrated version of the operating system with SP2.
2. To create an image, click Start, click Run, and then type:
risetup.exe /add
3. The Remote Installation Services Setup Wizard appears. Follow the instructions in the wizard. When the Installation Source Files Location page prompts you for the image source, enter the path to the shared folder that contains the integrated version that you created in Step 1.
4. A box appears showing the progress of the installation. After the RISetup image is complete, you can install the image on each server as described in Remote Installation Services on the Microsoft TechCenter Web site.
Creating a Remote Installation Preparation (RIPrep) image to deploy to other serversIf you want to add additional programs or settings to your integrated installation image, you must have a CD–based image of Windows Server 2003 with SP2 on your RIS server. Note that you cannot use the /integrate option to integrate SP2 directly into an existing CD-based image or a RIPrep image.
To update existing RIPrep images
1. Use RIS to install the RISetup image on your computer.
2. Add the additional programs and settings that you want to include in the image.
3. Run RIPrep to create an image on the RIS server. For instructions on how to run RIPrep on RIS servers running Windows Server 2003, see:
•Remote Installation Services (
http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=36940 )
•Automating and Customizing Installations (
http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=44324 )
4. You can now deploy your RIPrep image to other servers.
NETWORK:-Installing SP2 using source files that are located on a network share
To install SP2 from the network, first extract the installation files to a shared distribution folder. Then install SP2 on each computer using these files.
To install the service pack using a network share
1 Connect to the network or computer where you want to create the distribution folder.
2 In the shared folder, create a distribution folder.
For example, to create a distribution folder named WS2003SP2, type mkdir Drive:\WS2003SP2 at the command prompt (Drive: represents the drive where you want to store the distribution folder).
3 To extract the files to the distribution folder, type the following at the command prompt, where Path is the location of the distribution folder:
WindowsServer2003-KB914961-SP2-XXX-LLL.exe /X:Path
4 For each computer that you plan to update, back up the files and close programs before you continue (unless you plan to force programs to close during the installation).
5 To install the service pack from the shared distribution folder, run Update.exe. For example, to install from a distribution folder named WS2003SP2, type the following at the command prompt using the desired
command-line options :
Drive:\WS2003SP2\i386\Update\Update.exe
6. Follow the instructions in the Setup Wizard.
7. After Update.exe has completed, restart the computer to complete the installation. SP2 will not be fully installed until you restart your computer.
8. If you disabled your antivirus software, enable it after you restart the computer.
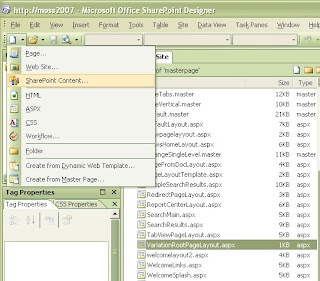
 Then open folder master page and click on page layout
Then open folder master page and click on page layout 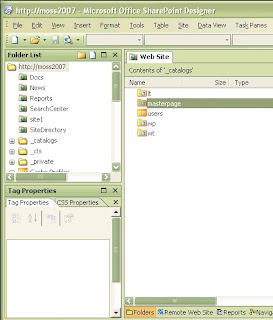

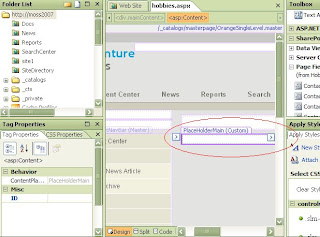 There you will see the place holder part
There you will see the place holder part 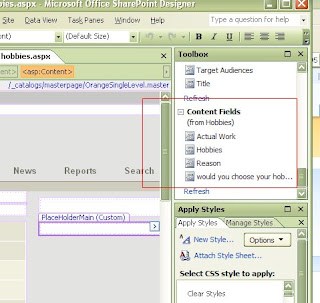
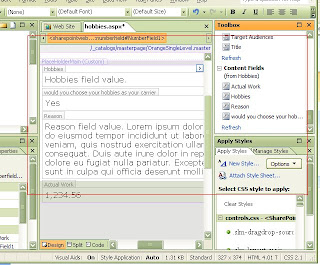 Save this page check in the ocument and you are done, you have sucessfully made your own content type,
Save this page check in the ocument and you are done, you have sucessfully made your own content type,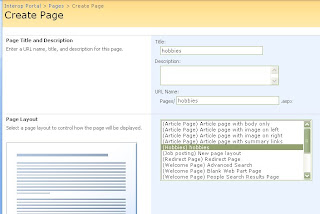 You see your creation listed there
You see your creation listed there 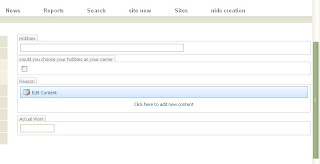
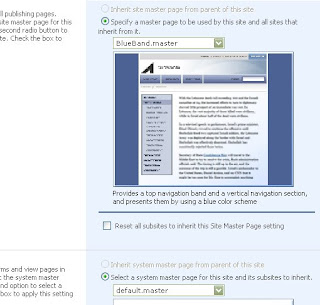 Select the page and check on check box that says inheriting to subsites. Now your page is changed to a brand new master page
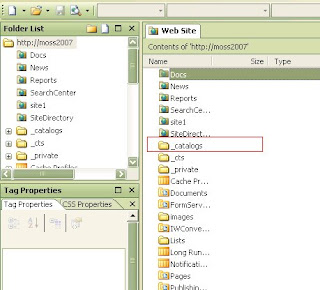
Select the page and check on check box that says inheriting to subsites. Now your page is changed to a brand new master page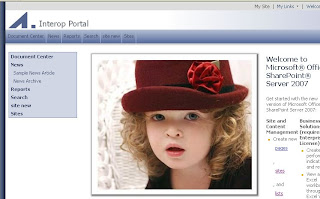 Now after this you have to open this site in sharepoint designer Then Open the Site in Designer and open folder called _catalogs folder and double click the Master page folder.
Now after this you have to open this site in sharepoint designer Then Open the Site in Designer and open folder called _catalogs folder and double click the Master page folder.
 Limitations are that I didnot find it being implemented on the new page that i created even after changing it to master page
Limitations are that I didnot find it being implemented on the new page that i created even after changing it to master page